Sources: Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge; CP staff An investigation based at Massachusetts Institute of Technology has revealed the potential of portland cement, water and carbon black, a common industrial mineral resembling ultrafine charcoal, to create a supercapacitor material suited to low-cost storage of energy derived from solar, wind and tidal power sources. MIT and Harvard University researchers see the…
Read MoreTag: cement hydration
MICROSTRUCTURE-BASED KINETICS MODEL
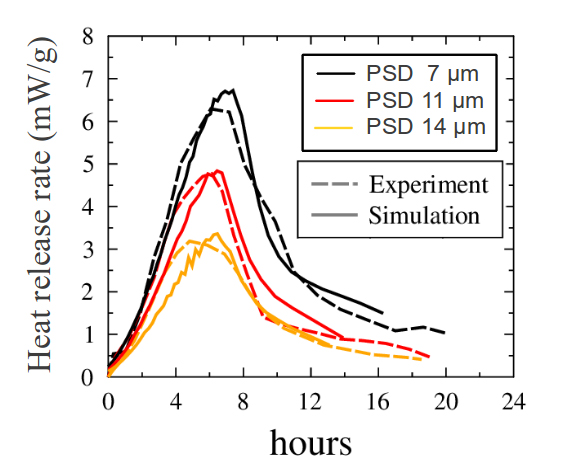
A November 2013 CSHub research profile letter, “Early hydration: A local business,” charts calorimetry (heat measurement) curves from tricalcium silicate paste experiments—with specimens of three particle size distributions (PSD)—to support a proposed model of microstructure-based kinetics. It suggests a “reaction zone” extending a few micrometers in from the cement particle surface, and can reconcile longtime observations on PSD and water/cement ratio.
Read More